
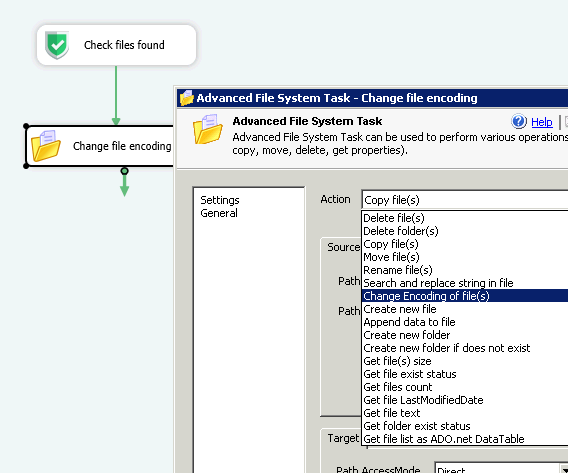
#Utf 16 utf 8 converter code#
(For example, modify the default value there or pass -D U_CHARSET_IS_UTF8=1 as a compiler flag.) This will change most of the implementation code to use dedicated (simpler, faster) UTF-8 code paths and avoid dependencies on the conversion framework. If it is known that the default charset is always UTF-8 on the target platform, then you should #define U_CHARSET_IS_UTF8 1 in or before unicode/utypes.h. Since this could be one of many charsets, and the charset can be different for different processes on the same system, ICU uses its conversion framework for converting to and from UTF-16. ICU has many functions that take or return char * strings that are assumed to be in the default charset which should match the system encoding. (Among conversion methods, APIs with a charset name are more convenient but internally open and close a converter ones with a converter object parameter avoid this.) UTF-8 as Default Charset These can be used for UTF-8, but are not as efficient or convenient as the fromUTF8()/ toUTF8()/ toUTF8String() methods mentioned above. Note: icu:: UnicodeString has constructors, setTo() and extract() methods which take either a converter object or a charset name. The conversion functions in unicode/ucnv.h are intended for very flexible handling of conversion to/from external byte streams (with customizable error handling and support for split buffers at arbitrary boundaries) which is normally unnecessary for internal strings. (Also u_strFromUTF8(), u_strToUTF8() and u_strFromUTF8Lenient().) In C, unicode/ustring.h has functions like u_strFromUTF8WithSub() and u_strToUTF8WithSub().
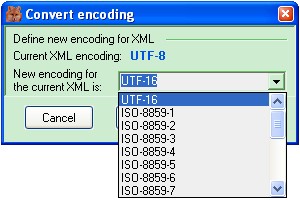
The simplest way to use UTF-8 strings in UTF-16 APIs is via the C++ icu::UnicodeString methods fromUTF8(const StringPiece &utf8) and toUTF8String(StringClass &result). (Input length=-1 means NUL-terminated, output is NUL-terminated if there is space, output overflow is handled with preflighting for details see the parent Strings page.) Some newer APIs take an icu::StringPiece argument and write to an icu::ByteSink or to a string class object like std::string. Some data structures are designed to work equally well with UTF-16 and UTF-8.įor UTF-8 strings, ICU normally uses (const) char * pointers and int32_t lengths, normally with semantics parallel to UTF-16 handling. While most of ICU works with UTF-16 strings and uses data structures optimized for UTF-16, there are APIs that facilitate working with UTF-8, or are optimized for UTF-8, or work with Unicode code points (21-bit integer values) regardless of string encoding. In Java, all strings are encoded in UTF-16, except for conversion from bytes to strings (via InputStreamReader or similar) and from strings to bytes (OutputStreamWriter etc.). Note: This page is only relevant for C/C++. This site uses Just the Docs, a documentation theme for Jekyll. Updating MeasureUnit with new CLDR data.The low surrogate 16-bits encoding will be “0xDF62”ħ. The high surrogate 16-bits encoding will be “0xD852”Ħ. Adding “0xDC00” to low surrogate. We have to subtract all 20 binary bits into 2 part.ĥ. We have to subtract 0x10000 from the code points. In case of a code points is over than U+10000, UTF16 encoding requires 2 bytes of 16 bits binary.Search for “𤭢” code point, which is “U+24B62”.Example – Encode string “ 𤭢” to UTF16 hexadecimal.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
